
2.5 milligrams vitamin C (4 percent DV).0.1 milligrams vitamin B6 (5 percent DV).0.8 milligrams pantothenic acid (8 percent DV).

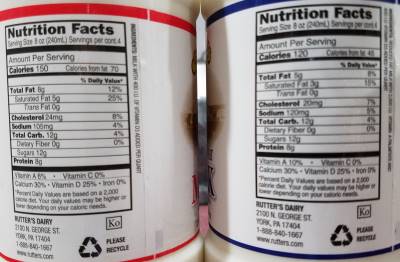
407 milligrams potassium (12 percent DV).0.9 micrograms vitamin B12 (16 percent DV).0.3 milligrams riboflavin (20 percent DV).247 milligrams phosphorus (25 percent DV).One cup of non-fat milk contains the following nutrients: Each serving contains a low amount of skim milk calories but is rich in protein and important micronutrients like calcium, phosphorus and riboflavin. Like other types of milk, skim milk is highly nutritious. If using skim milk in place of whole milk, you may need to adjust your recipe by adding a bit of extra butter or oil to improve the taste and texture. Whole milk can also help add moisture to baked goods to keep them tender and soft. Most cooking and baking recipes call for whole milk rather than skim, as the extra fat can enhance the flavor and texture of the final product. Because it’s higher in fat, whole milk contains a higher amount of omega-3 fatty acids per serving than skim or low-fat varieties. Omega-3 fatty acids are a type of essential fatty acid that have been shown to improve immune function, alleviate inflammation, enhance heart health and more. skim milk nutrition facts as well, especially when it comes to the amount of omega-3 fatty acids present in each serving. There are a few other minute variations between the whole milk vs. One cup of skim milk contains about 86 calories, for example, while a cup of whole milk provides 146 calories. While whole milk usually contains approximately 3.25 percent milk fat, skim varieties generally contain less than 0.5 percent.īecause fat is high in calories, there are fewer calories in skim milk than whole milk. Whole milk has not been altered or modified in any way, whereas other varieties like low-fat or skim milk are produced by removing a portion of fat from the milk. The main difference between skim milk vs. Related: What Is Lactase? How It Helps Manage Lactose Intolerance & More Skim Milk vs. Canned, evaporated and sweetened condensed skim milk varieties are also widely available. Skim milk powder, for instance, is produced by removing the water from skim milk, resulting in a product with a much longer shelf-life. Similar to other types of milk, skim milk can be found in several different forms. Because of its lower fat content, it is also much lower in calories, with just 58 percent of the amount of calories of whole milk in each cup.

Skim milk, also called nonfat milk, is a type of milk that typically contains 0.5 percent milk fat. Meanwhile, low-fat and skim milk are each produced by removing a portion of the fat from whole milk, resulting in a final product that is lower in total fat and calories. Whole milk contains the highest amount of fat, with around 3.25 percent milk fat. Take a stroll down the dairy aisle of your local supermarket and you may notice that there are several types of milk available, each of which varies based on its respective fat content.
#WHOLE MILK VS SKIM MILK NUTRITION FACTS PLUS#
Keep reading for a few of the top skim milk benefits and disadvantages, plus some simple recommendations for your next shopping trip. While it’s true that skim milk is low in fat and a great source of several nutrients, there are some drawbacks to consider with this dairy product, along with several reasons you may want to opt for whole milk instead. However, it has also become a controversial ingredient, with new studies emerging left and right discussing either why skim milk is bad or debating its potential impact on bone strength, heart health and more. Skim milk has been considered a classic breakfast staple for decades.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
